Using Linux and other free software, it's possible to revive an older but perfectly functioning printer as an AirPrint printer, allowing simple driverless printing from your iPhone and other devices. This article outlines a solution using the following:
- A Linux distro, I use Fedora release 35
- Common UNIX Printing System or CUPS for network printing
- Avahi for multicast DNS (mDNS) or DNS Service Discovery (DNS-SD) aka Bonjour
In this article we connect the print server to the printer over the network, which requires a printer with a network interface possibly via a network card. A print server is any physical or virtual machine running Linux with CUPS and Avahi installed, in my case it's a VM running on VMWare on an HP ProLiant DL380G7 rack server. The printer can also be physically connected to the print server through USB, serial, parallel, or any other mechanism supported by CUPS. It could even be an authenticating IPP print service being accessed over the Internet.
Printing from your iPhone utilizes AirPrint, an Apple technology built on several standards: Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) and mDNS. IPP, controlled by the Printer Working Group provides a standard way to send jobs to a printer, track jobs, receive errors, etc; Multicast DNS (mDNS) or DNS Service Discover (DNS-SD), also called zero configuration networking or ZeroConf1, is a way to advertise services on the local network alongside capabilities information. IPP Everywhere is an open standard which works similarly to AirPrint, and is compatible with it.
Installing Linux on your chosen target system is out of scope for this article, in my case I uploaded an ISO to VMWare and booted a new VM with it as the CD-ROM, once installed I did some housekeeping:
# Connecting over SSH as my user
; mkdir -p .ssh
; chmod 700 .ssh/
; cd .ssh/
# Add my SSH public key so I can login without a password
; echo 'my-public-key' >> authorized_keys
; chmod 600 authorized_keys
# Allow VMWare better interop with the guest
; sudo dnf install open-vm-tools
Goal
Our goal print job flow is the following:
In more detail:
- Avahi will send multicast UDP packets which are received by every device on the local network. These packets contain the
SRVrecords which define our IPP Everywhere (AirPrint) service and include information like the IP and port of the Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) service CUPS provides, the capabilities of our printer, etc. - Our iPhone receives this
SRVrecord and updates its database of local services. When we open a print dialogue, we can choose from these advertised IPP services presented as printers. - When we print a document, our iPhone sends the PDF or other common raster format over IPP to our CUPS server, along with metadata such as single-sided or two-sided printing, etc. CUPS returns a job id for the submission and our iPhone can check the status of the job and report any errors to us via IPP.
- CUPS transforms the job from PDF or common raster format, through filters, into a format that the printer driver can understand such as PostScript. The driver then converts this format to a language the printer can understand such as HP Printer Command Language (PCL) or HP Raster Transfer Language.
- This final (usually raster) format is sent to the printer over the network via AppSocket (TCP on port 9100) to the printer for processing. The printer may report errors or a successful print, which CUPS will report via IPP when our iPhone checks on the job.
AppSocket is a protocol developed by Tektronix in which a driver can talk to a printer over a TCP connection to port 9100 on the printer's network interface -- the protocol is also called JetDirect (because of its usage with JetDirect cards) or RAW. The HP printer listens for commands from network connections as if it were directly connected to a PC over serial or parallel, supporting the same formats such as Adobe PostScript, HP Printer Command Language (PCL), or its subset HP Raster Transfer Language (RTL).
It is imperitive that the printer's network interface not be accessible from the Internet. Access to the printer network interface should be limited to the local network, and preferably only accessible by the print server via VLAN or physical network partition. Since it has no authentication mechanism, AppSocket will accept anything sent to it and print it. You can navigate to your printer's IP on port 9100, e.g. http://printer.home.arpa:9100, and the printer will print out the incoming HTTP request as if it were a print job.
Installing and Configuring
To install CUPS and Avahi, you should be able to use your distro's package manager:
; sudo dnf install cups
# These may be unnecessary
; sudo systemctl enable cups --now
; sudo systemctl enable avahi --now
The cups package installs Avahi through its dependency on cups-browsed on Fedora, but may not on all systems.
If you use a firewall, you need to poke some holes to allow your devices to communicate with CUPS over your local network:
; sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service ipp --permanent
; sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service mdns --permanent
; sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Now IPP is one of the allowed services:
; sudo firewall-cmd --list-services
... ipp mdns ...
If you're using an HP printer, you'll want to install hplip so that CUPS can use those drivers:
; sudo dnf install hplip
Configuring CUPS
To configure CUPS to accept traffic from other network devices, we need to edit /etc/cups/cupsd.conf, by replacing the Listen directive for localhost with a general Port directive:
#Listen localhost:631
Port 631
To allow all (even unauthenticated admin) access from your local network to the Web UI, add this to /etc/cups/cupsd.conf (more information at Red Hat and man cupsd.conf):
LogLevel info
MaxLogSize 1m
ErrorPolicy stop-printer
ServerAlias *
# Allow remote access
Port 631
Listen /run/cups/cups.sock
WebInterface Yes
IdleExitTimeout 60
<Location />
Allow @LOCAL
</Location>
A LogLevel of info will give you more information on when the Web UI or IPP service is being used. The Location block is required to allow printing from the local network. Omitting any Policy blocks seems to allow any user to access the admin Web UI without authentication. Disabling Browsing means CUPS won't produce mDNS entries of its own, instead we'll do that manually so they work with AirPrint. You'll need to restart CUPS to see config changes reflected:
; sudo systemctl restart cups.service
At this point you'll want to configure your printer in CUPS through the Web UI:
- if you have an older printer and will be using "classic drivers", follow these directions,
- for a more modern printer which supports driverless printing follow these directions.
Remember to check the share printer option, otherwise CUPS will restrict access to the printer.
You can also add printers via the /etc/cups/printers.conf file while cupsd is stopped, if you also add a corresponding /etc/cups/ppd PPD file of the same name. Editing the printers.conf file manually is not recommended, and the options available are undocumented2. See this incomplete documentation from Apple for moree info on each option. Below is mine:
NextPrinterId 3
<DefaultPrinter printer>
PrinterId 1
UUID urn:uuid:fb026ac7-8613-3eb4-5b51-9749073f7704
AuthInfoRequired none
Info HP LaserJet 4100N
Location Office
MakeModel HP LaserJet 4100 Series hpijs pcl3, 3.21.2
DeviceURI socket://printer.home.arpa
State Idle
StateTime 1686858786
ConfigTime 1680818482
Type 8425500
Accepting Yes
Shared Yes
JobSheets none none
QuotaPeriod 0
PageLimit 0
KLimit 0
OpPolicy default
ErrorPolicy stop-printer
Attribute marker-colors none
Attribute marker-levels 27
Attribute marker-names Toner Cartridge HP C8061X
Attribute marker-types toner
Attribute marker-change-time 1686858786
</DefaultPrinter>
<Printer designjet>
PrinterId 2
UUID urn:uuid:b691f515-4a45-35da-5707-debfda29d917
Info HP DesignJet 650C
Location Office
MakeModel HP DesignJet 650C Foomatic/dnj650c (recommended)
DeviceURI socket://designjet.home.arpa
State Idle
StateTime 1683579922
ConfigTime 1671595356
Type 8450060
Accepting Yes
Shared Yes
JobSheets none none
QuotaPeriod 0
PageLimit 0
KLimit 0
OpPolicy default
ErrorPolicy stop-printer
</Printer>
Both printers I have configured are communicating via the AppSocket protocol via socket:// aka TCP port 9100 over the local network. I use pfSense running on a VM as my home router, which provides DNS resolution via .home.arpa, the recommended home DNS suffix, which is why they aren't IP addresses. I also recommend configuring your router to assign static IPs (through DHCP) to network devices like printers so that configurations like this can use the IP address. Alternatively, if your printer or network card is sophisticated enough (like the later EIO careds), you can use an mDNS address with a URI like dnssd://HP-LaserJet-4100n._pdl-datastream._tcp.local (optionally with ?uuid=). The problem with using mDNS for this is that now your printer will be advertising itself and will show up in the Mac print dialogue if it advertises _ipp._tcp., so I disable mDNS on the printer itself.
You will also need a PPD under /etc/cups/ppd that is either created via the CUPS UI wizard or uploaded manually (e.g. when fetched from openprinting.org). CUPS PPD files support extensions atop Adobe PPD version 4.33.
CUPS will eventually deprecate using printer drivers with PPDs, in favor of using a Printer Application (as described in A New Way to Print in Linux) or PAPPL. A PAPPL-based app is one that presents an IPP interface which accepts PDFs and then converts them (the same way that CUPS does internally) to the custom or raster format of the actual printer, and sends it over the appropriate interface. There are already printer apps for HP printers that use hplip (such as my HP LaserJet 4100n), hp-printer-app, for printers that use a GhostScript driver (such as my HP DesignJet 650c), ghostscript-printer-app, and for printers that use a GutenPrint driver, gutenprint-printer-app. I've yet to migrate to these printer apps but plan to do so, I've run into the following issues:
- Through
snap, I can't configurehp-printer-appto consider its hostnamehp-printer-app.home.arpa. This means the UI can be available at a custom local domain and proxied via nginx, but links will redirect tolocalhost:8000. - Once I make
:8000available via firewall and add an Avahi service file to advertise AirPrint, printing via it fails withGet-Jobs client-error-not-found (printer-uri ipp://misc.local.:8000/printers/HP_LaserJet_4100n not found.). I need to know how to construct the printer URI for therpfield in the service definition.
After the printer is configured, ensure you print a test page to ensure CUPS can communicate to the printer and the chosen driver works with your model.
Configuring Avahi
Once that's done, you'll need to generate your Avahi service config. It's not difficult to write on manually, the below is what I use for my HP LaserJet and is at /etc/avahi/services/AirPrint-printer.service:
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<!DOCTYPE service-group SYSTEM 'avahi-service.dtd'>
<service-group>
<name replace-wildcards="yes">HP LaserJet 4100N</name>
<service>
<type>_ipp._tcp</type>
<subtype>_universal._sub._ipp._tcp</subtype>
<port>631</port>
<txt-record>txtvers=1</txt-record>
<txt-record>qtotal=1</txt-record>
<txt-record>UUID=AFEB3961-F48A-499A-B6C5-605A723CECF4</txt-record>
<txt-record>Transparent=T</txt-record>
<txt-record>Binary=T</txt-record>
<txt-record>TBCP=T</txt-record>
<txt-record>kind=document,envelope</txt-record>
<txt-record>Duplex=T</txt-record>
<txt-record>URF=DM3</txt-record>
<txt-record>rp=printers/printer</txt-record>
<txt-record>note=Office</txt-record>
<txt-record>product=(GPL Ghostscript)</txt-record>
<txt-record>printer-state=3</txt-record>
<txt-record>printer-type=0x409014</txt-record>
<txt-record>pdl=application/octet-stream,application/pdf,application/postscript,application/vnd.cups-raster,image/gif,image/jpeg,image/png,image/tiff,image/urf,text/html,text/plain,application/vnd.adobe-reader-postscript,application/vnd.cups-pdf</txt-record>
</service>
</service-group>
You can also use the airprint-generate.py script by Timothy Fontaine. To get airprint-generate.py running, you'll need to install some dependencies:
; sudo dnf install pip gcc clang libpython python3-devel cups-devel
; pip3 install wheel pycups
Then run the script and copy the output to /etc/avahi/services/.
The pdl must include image/urf to work with AirPrint, from Apple's documentation:
AirPrint devices don’t browse for all IPP printers—they browse only for the subset of IPP printers that support Universal Raster Format (URF).
The service for my HP DesignJet is very similar, but I made some changes (some necessary, some for curiosity's sake). I'll illustrate the changes I made:
I replaced the name with
<name replace-wildcards="yes">HP DesignJet 650C</name>
The UUID with
<txt-record>UUID=3C84F9A5-A870-475F-A758-43DDF9B290EC</txt-record>
Added a TLS record, changed kind to reflect a large format printer, toggled Duplex off, toggled Color on, and changed PaperMax and PaperCustom to illustrate that the printer can print to large formats:
<txt-record>TLS=1.2</txt-record>
<txt-record>kind=large-format,roll</txt-record>
<txt-record>Color=T</txt-record>
<txt-record>PaperMax=>isoC-A2</txt-record>
<txt-record>PaperCustom=T</txt-record>
Changed rp to the printer name, added a ty field:
<txt-record>rp=printers/designjet</txt-record>
<txt-record>ty=HP DesignJet 650C</txt-record>
and omitted the printer-state and printer-type fields.
If you have a Mac, you can use the Discovery app to see mDNS services available on the local network; which is useful for debugging as this is what your iPhone sees when it searches for nearby AirPrint-enabled printers.
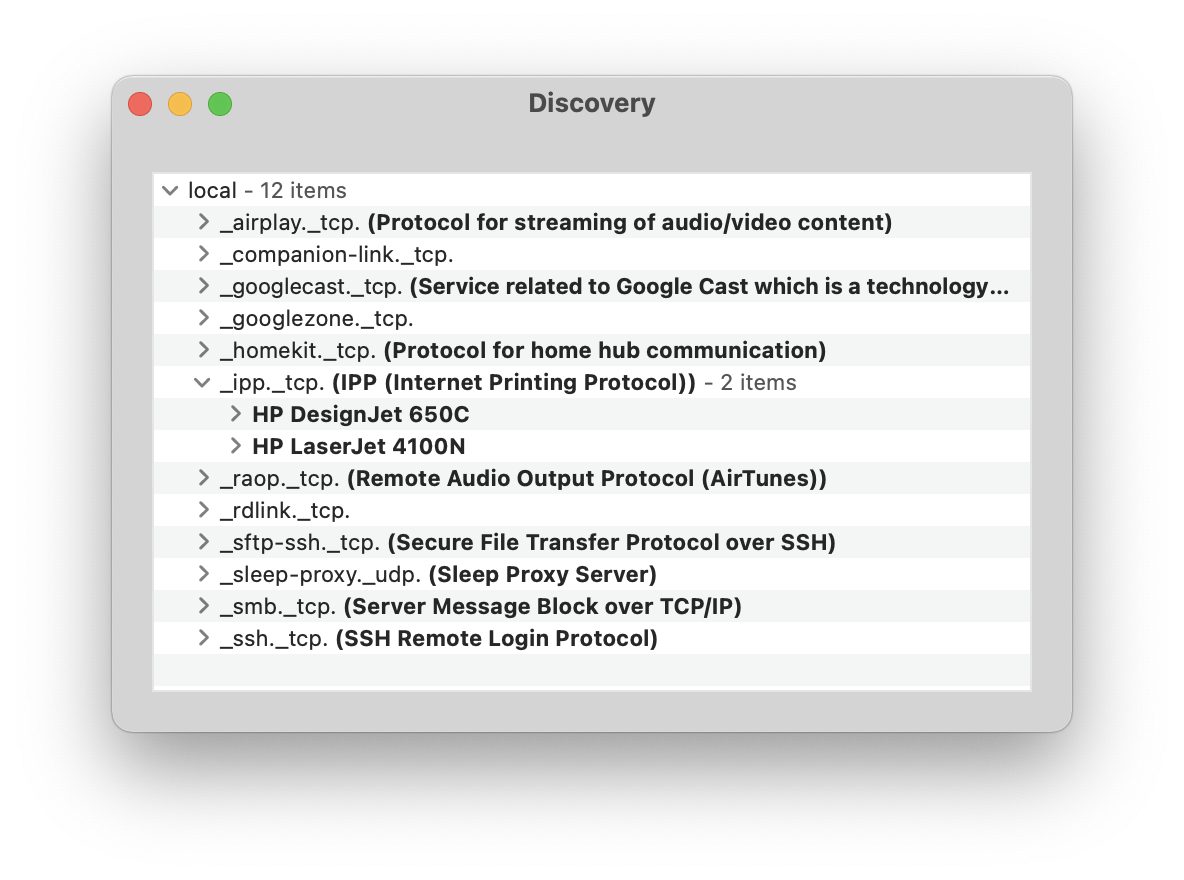
The important services are under _ipp._tcp., you should see one per Avahi service file. Expanding a service should display each txt-record option as a row.
If Printer Sharing is enabled in CUPS and Avahi is installed, an IPP service will be advertised via mDNS but it won't have the necessary TXT records for AirPrint which indicate what capabilities the printer has. You should disable Printer Sharing to avoid duplicate printers (one driver-less, one conventional Bonjour) showing on a Mac. More information on each TXT record is available in the Bonjour Printing specification, in Table 2 on page 17 for description records and in Table 3 on page 23 for capability records.
Once your Avahi service is configured, you should see your printer on your iPhone. Try printing a page of a PDF, if it prints successfully congratulations. If not,
- If an error is returned, determine if it is a printer fault or a software issue.
- Ensure printing a test page from CUPS works, so that we can rule out a CUPS issue.
- Ensure the Avahi service being advertised points at your CUPS server and is accessible from your local network. Ensure the firewall is not blocking mDNS or IPP.
- Use
ipptoolto print a test job to the IP, port, andrppath that the mDNS service advertises. - If the request is reaching CUPS, look at the CUPS admin UI under printers and jobs for job status
- Ensure the printer isn't paused (by default it will be paused after a failed job)
- Look at the
systemctl status cups.serviceoutput and logs
Using Nginx as a CUPS UI proxy
If you'd like to make CUPS available on the standard HTTP/HTTPS port, you can install nginx:
; sudo dnf install nginx
For a TLS-enabled server, add this configuration to /etc/nginx/conf.d/cups.conf:
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name cups.home.arpa;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name cups.home.arpa;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:631/;
proxy_set_header Host "127.0.0.1";
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forward-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /404.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
With a TLS-enabled server, you need to create some PKI and add the cert to both the server running CUPS and your laptop. The easiest way to set up PKI is using cfssl. By setting server_name to cups.home.arpa, a DNS alias I added in my router (pfSense) which points to the same IP that DHCP assigns to the VM, I'm able to host multiple web interfaces for different sites on the same VM.
Why print in 2023?
Aside from the ocassional form, I often print recipes from the NYT Cooking app. Their iOS app produces beautiful and readable print-outs in crisp black-and-white serif text, with ingredients on the left-hand column and steps on the right. Printing recipes allows me to dirty my hands cooking without needing to constantly unlock my phone.
-
For more information about mDNS, see the book Zero Configuration Networking: The Definitive Guide. ↩︎
-
CUPS parses the
printers.conffile in thecupsdLoadAllPrintersroutine, which contains the names of the options.man printers.confnotes: "The name, location, and format of this file are an implementation detail that will change in future releases of CUPS." ↩︎ -
Adobe no longer hosts a copy of the spec, but MIT hosts a copy of several Adobe tech notes; which can be accessed by replacing the file name in the URL with the orignal Adobe file name e.g.
5003.PPD_Spec_v4.3.pdf. ↩︎
See comments on Hacker News.